1 Why amcat
Say, there has been a media frenzy recently about a political scandal. You know that it started with a revelation by an anonymous poster on Reddit, spread through social media, and was investigated by respectable media outlets, which created public pressure until the topic was discussed in your country’s parliament and a minister or two had to step down. You quickly realise that the case is a treasure trove for investigating your political system and testing several media theories in the process.
You spin up a new instance of the amcat suite on your research server or a new cloud instance and start to collect data through APIs of social media websites, media monitoring sites and scrapers and store everything in the amcat database. You share your data with collaborators, using fine-grained data access control since some of the scraped content is copyrighted. A new research assistant with some knowledge about the case but no technical training starts digging through the data using amcat’s user interface and publicly available dashboard to search for potentially relevant terms and queries. One of your collaborators builds on this by producing time-series models and plots in R.
You decide to dig deeper into the content and start training coders and deploy coding tasks through amcat’s annotation tool. Coders get through the task quickly as they can access the interface on their phones and code on their bus commutes or whenever else they feel like it. You use your amcat server to preprocess the data and train and validate a heap of advanced machine learning models that complete the coding task of all documents. Your analysis reveals new mechanisms and confirms some of the theories you worked with.
After writing up a paper, you submit your results to a journal. The editor asks for replication code and data, so you simply share your R or Python scripts and grant temporary access to your amcat server for a researcher tasked with replicating your results.
After publication, a newspaper picks up your results, leading some interested citizens to play with your dashboard. Even though users do not have access to the full text for copyright reasons, they can query different combinations of keywords, which makes your research transparent for a wider audience. Since the annotations and the preprocessed texts are also available, someone finds they get even better validation scores using a newly created algorithm.
1.1 What is amcat?
The amcat-suite consists of several packages for text analysis. It has two main goals: to standardize text analysis tasks with easy to use software, while offering quality-of-life features for power users. It consists of several different software packages, which are usually used together:
amcat4takes care of document storage, provides fine-grained data access control (e.g., to restrict access to the parts of a dataset which are copyrighted, proprietary or (privacy-)sensitive) and supports fast queries using Elasticsearchmiddlecatprovides authentication methods to support the fine-grained data access control built intoamcat4(e.g., to make datasets available for which data owners have restricted full text access)amcat4clientoffers a user interface, which makes it easy to query documents fromamcat4via a web interface, share data with collaborators or the public and present your corpora to stakeholders, the community or the publicamcat4apiclientprovides bindings to manage and query corpora from thePythonprogramming language viaamcat4’s REST APIamcat4rprovides bindings to manage and query corpora from theRprogramming language viaamcat4’s REST API
These core packages can be extended by powerful addons which provide additional features:
annotinderwhich let’s you manually annotate documents with an appealing web interface (which also looks great on mobile!) and the possibility to deploy it to the web. There is also an R client!nlpipecan be used for advanced document pre-processing and machine learning tasks. You can’t share your full text? How about lettingnlpipeapply word embeddings on your corpus and share the embedding instead of the full text!
You can use many of these packages individually or you create a full setup, which would look something like this:
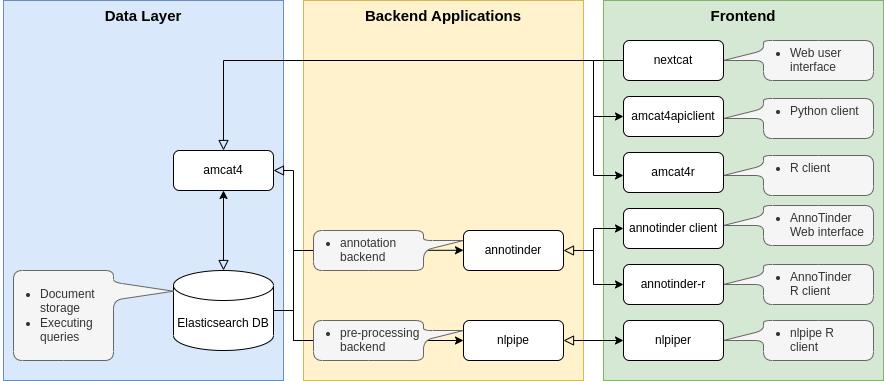
It might seem like this is overly complicated, given that all of the features are also available in other software packages, some of which you will also be familiar with already. However, the main reason that functions are split between different software modules is to make development easier and more transparent. If you are only interested in amcat’s capabilities, you can use it on our servers or conveniently install everything at once through docker.
If you want to learn more about the project, have a look at the about chapter.